Glossary
- ASN.1
Abstract Syntax Notation 1 is a standard description language for specifying serialisation and deserialisation of data structures in a portable and cross-platform way.
- bytes-like object
All the types that implement the buffer protocol. That includes
str(only on python2),bytes,bytearray,array.arrayandmemoryviewof those objects. Please note thatarray.arrayserialisation (converting it to byte string) is endianess dependant! Signature computed overarray.arrayof integers on a big-endian system will not be verified on a little-endian system and vice-versa.- compressed
The public point representation that uses half of bytes of the uncompressed encoding (rounded up). It uses the first byte of the encoding to specify the sign of the y coordinate and encodes the x coordinate as-is. The first byte of the encoding is equal to 0x02 or 0x03. Compressed encoding of NIST256p public key will be 33 bytes long.
- DER
Distinguished Encoding Rules, the way to encode ASN.1 objects deterministically and uniquely into byte strings.
- ECC
Elliptic Curve Cryptography, a term for all the different ways of using elliptic curves in cryptography. Also combined term for ECDSA, EdDSA, ECDH.
- ECDH
Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman
- ECDSA
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
- EdDSA
Edwards curve based Digital Signature Algorithm, the alternative digital signature algorithm that’s used for Curve25519 or Curve448
- hybrid
A combination of uncompressed and compressed encodings. Both x and y coordinates are stored just as in compressed encoding, but the first byte reflects the sign of the y coordinate. The first byte of the encoding will be equal to 0x06 or 0x7. Hybrid encoding of NIST256p public key will be 65 bytes long.
- PEM
The acronym stands for Privacy Enhanced Mail, but currently it is used primarily as the way to encode DER objects into text that can be either easily copy-pasted or transferred over email. It uses headers like
-----BEGIN <type of contents>-----and footers like-----END <type of contents>-----to separate multiple types of objects in the same file or the object from the surrounding comments. The actual object stored is base64 encoded.- raw encoding
Conversion of public, private keys and signatures (which in mathematical sense are integers or pairs of integers) to strings of bytes that does not use any special tags or encoding rules. For any given curve, all keys of the same type or signatures will be encoded to byte strings of the same length. In more formal sense, the integers are encoded as big-endian, constant length byte strings, where the string length is determined by the curve order (e.g. for NIST256p the order is 256 bits long, so the private key will be 32 bytes long while public key will be 64 bytes long). The encoding of a single integer is zero-padded on the left if the numerical value is low. In case of public keys and signatures, which are comprised of two integers, the integers are simply concatenated.
- set-like object
All the types that support the
inoperator, likelist,tuple,set,frozenset, etc.- short Weierstrass curve
A curve with the curve equation:
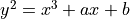 . Most popular
curves use equation of this format (e.g. NIST256p).
. Most popular
curves use equation of this format (e.g. NIST256p).- uncompressed
The most common formatting specified in PKIX standards. Specified in X9.62 and SEC1 standards. The only difference between it and raw encoding is the prepending of a 0x04 byte. Thus an uncompressed NIST256p public key encoding will be 65 bytes long.